3d printed heart model
TaVon Cates
Did you know that on average, 21 people die every day waiting on an organ transplant? According to the American Transplant Foundation, there is more than 123,000 people in the United States currently waiting on an organ transplant to save their lives and someone is added to that list every 12 minutes!
The American Transplant Foundation also says that over 6,500 people die every year waiting on the organ transplant. Many people are organ donors, but a lot of their organs are not donated until after they are dead. Now with the average life expectancy at almost 80 years, help comes either too late or not at all for many people.
The increasing in technology in the modern age may have a solution for this. A technique that has been around for quite some time and the uses are ever changing, 3-Dimensional printing.
Here we see a 3D Printed Burger and Fries.
3D printing is a technique in which objects are constructed from digital data. It almost like a regular printer, except it prints in layers and takes a little longer than an average printer. Many scientists are taking this technique into the medical field.
With the help of 3D printing, 3D printed organs have become a reality. However, because this technology is relatively new in the field, there are still a few kinks being worked out.
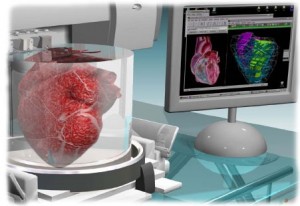
3D printing has been especially helpful for cardiologists, especially those dealing with congenital heart disease. 3D printing has helped to produce accurately printed, realistic, 3D hearts. These 3D models can help increase procedural efficiency because cardiologist would be able to have a model of the patients’ heart to examine and “operate” on before the actual procedure takes place. This procedure will also increase patient safety because the doctors would have already done the procedure before.
One instance of this procedure being used would be the case of four month old Lucy. She suffered from heart failure, which starved her Kidney’s. Her father offered to donate his Kidney so she wouldn’t have to be on dialysis for the rest of her life.
The top left is Lucys’ father Kidney with actual living cells.
Doctors made a 3D model of both Lucy’s abdomen as well as her fathers’ kidney. With these, they made it clear to Lucy’s parents how such a large kidney would fit into such a small child. After doing the procedure on the 3D models, they were able to successfully transplant the Kidney into Lucy and change her life.
Another one of these life changing operations was done on four year old Mia. Her early childhood was filled would numerous bouts of colds, pneumonia, shortness of breath, etc. She wasn’t able to do many of the things that she loved such as dance. It was dismissed as asthma and she was prescribed asthma medications.
It took nearly 10 hospital stays for doctors to realize that the cause was much worse. They found that her aorta, the vessel that carries blood from the heart, and was pushing against the windpipe, which caused the shortness of breath and made it hard to swallow.
They were able to save her life because the hospital had recently gotten a 3D printer that makes EXACT replicas of organs. They saw the malformed aorta in the model and was able to ponder how they would fix the problem and do practice operations without actually harming the four year old.
Dr. Burke, the leading doctor, said that without the 3D replica, he would not have been as confident operating on Mia. He says that without the replica, the healing time as well as the pain and the experience for Mia would have been much worse.
One case study on the topic would be the Russian 3D printing company, 3D bioprinting solutions. The company has made an amazing advancement in 3D printing organs for transplants. In March of 2015, the company reported having made a working 3D model of a thyroid gland of a mouse. The replicated thyroid gland was able to carry out all of the functions that a regular thyroid gland would.
In November of 2015, the same company proudly announced that they had successfully transplanted the working thyroid gland into a live mouse and the mouse lived with no complications from the organ or the procedure.
This is a big accomplishment because regular thyroid transplants are not normally done because of all the complications that could come from the surgery such as infection. 3D organs are ideal for transplants because they are made up of the organism’s cells, therefore it has a much lower chance of being rejected by the body.
Organs are not the only thing that is able to be implanted thanks to 3D printing. Two men who suffered from cancer lives’ were changed thanks to 3D printing. One needed a sternum (chest plate) as well as a rib cage. Doctors were able to create a sternum and rib cage that exactly matched his anatomy through 3D printing. The second man lost half of his pelvis to cancer and was able to get a replica transplanted to complete the other half.
The 3D printed medal rib cage and sternum before and after transplanted into the patient.
21 people die every day because they cannot get the transplant they need to save their life. You have read about numerous people whose lives have been saved and changed thanks to 3D printing. The technology is still relatively new, so as it progresses and advances, tens of people will not lose their lives every day waiting on an organ or bone structure.